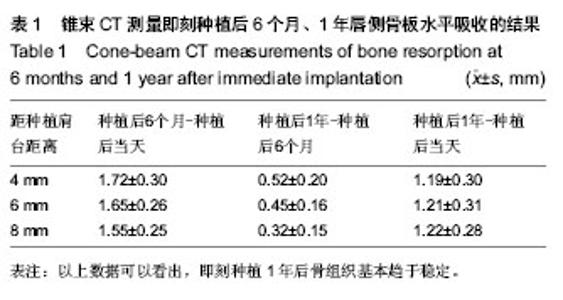
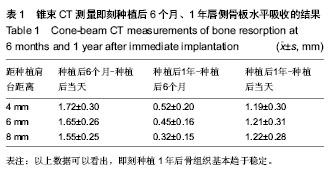
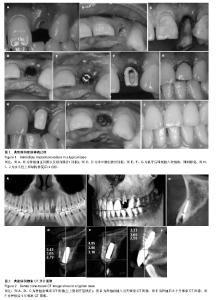
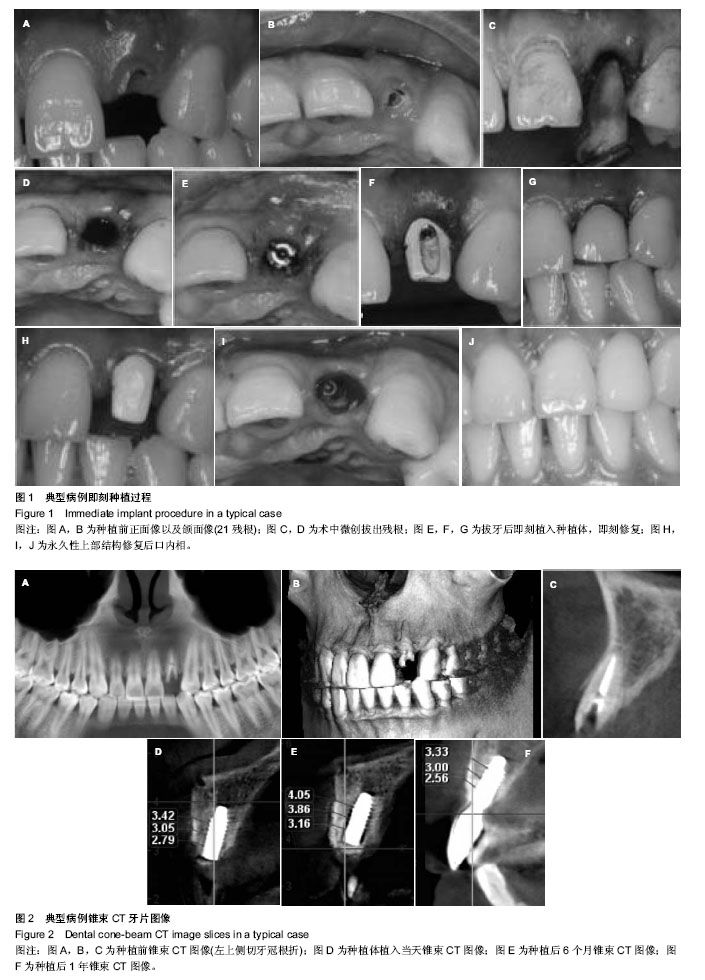
| [1] Schropp L, Wenzel A, Kostopoulos L,et al.Bone healing and soft tissue contour changes following single-tooth extraction: a clinical and radiographic 12-month prospective study.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2003;23(4):313-323.
[2] Schulte W, Kleineikenscheidt H, Lindner K, et al.The Tübingen immediate implant in clinical studies.Dtsch Zahnarztl Z. 1978;33(5):348-359.
[3] Buser D, Martin W, Belser UC.Optimizing esthetics for implant restorations in the anterior maxilla: anatomic and surgical considerations.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004;19 Suppl: 43-61.
[4] Vilhjálmsson VH, Klock KS, Størksen K,et al.Aesthetics of implant-supported single anterior maxillary crowns evaluated by objective indices and participants' perceptions.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011;22(12):1399-1403.
[5] Nevins M, Camelo M, De Paoli S,et al.A study of the fate of the buccal wall of extraction sockets of teeth with prominent roots.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2006;26(1):19-29.
[6] Evans CD, Chen ST.Esthetic outcomes of immediate implant placements.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008;19(1):73-80.
[7] Chen ST, Darby IB, Reynolds EC, et al.Immediate implant placement postextraction without flap elevation.J Periodontol. 2009;80(1):163-172.
[8] Buser D, von Arx T.Surgical procedures in partially edentulous patients with ITI implants.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2000;11 Suppl 1:83-100.
[9] Sanz M, Cecchinato D, Ferrus J,et al.A prospective, randomized-controlled clinical trial to evaluate bone preservation using implants with different geometry placed into extraction sockets in the maxilla.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21(1):13-21.
[10] Huynh-Ba G, Pjetursson BE, Sanz M,et al.Analysis of the socket bone wall dimensions in the upper maxilla in relation to immediate implant placement.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010; 21(1):37-42.
[11] Katranji A, Misch K, Wang HL.Cortical bone thickness in dentate and edentulous human cadavers.J Periodontol. 2007; 78(5):874-878.
[12] Araújo MG, Sukekava F, Wennström JL,et al.Tissue modeling following implant placement in fresh extraction sockets.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006;17(6):615-624.
[13] Denissen HW, Kalk W, Veldhuis HA,et al.Anatomic consideration for preventive implantation.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1993;8(2):191-196.
[14] Covani U, Crespi R, Cornelini R,et al. Immediate implants supporting single crown restoration: a 4-year prospective study.J Periodontol. 2004;75(7):982-988.
[15] Chen ST, Wilson TG Jr, Hämmerle CH.Immediate or early placement of implants following tooth extraction: review of biologic basis, clinical procedures, and outcomes.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004;19 Suppl:12-25.
[16] Sclar AG.Preserving alveolar ridge anatomy following tooth removal in conjunction with immediate implant placement. The Bio-Col technique.Atlas Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 1999;7(2):39-59.
[17] Paolantonio M, Dolci M, Scarano A,et al.Immediate implantation in fresh extraction sockets. A controlled clinical and histological study in man.J Periodontol. 2001;72(11):1560-1571.
[18] Buser D, Chen ST, Weber HP,et al.Early implant placement following single-tooth extraction in the esthetic zone: biologic rationale and surgical procedures.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2008;28(5):441-451.
[19] Botticelli D, Berglundh T, Lindhe J.Hard-tissue alterations following immediate implant placement in extraction sites.J Clin Periodontol. 2004;31(10):820-828.
[20] Araújo MG, Sukekava F, Wennström JL,et al.Ridge alterations following implant placement in fresh extraction sockets: an experimental study in the dog.J Clin Periodontol. 2005;32(6): 645-652.
[21] Botticelli D, Persson LG, Lindhe J,et al.Bone tissue formation adjacent to implants placed in fresh extraction sockets: an experimental study in dogs.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006; 17(4):351-358.
[22] Covani U, Cornelini R, Barone A.Buccal bone augmentation around immediate implants with and without flap elevation: a modified approach.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2008;23(5): 841-846.
[23] Sanz M, Cecchinato D, Ferrus J,et al.A prospective, randomized-controlled clinical trial to evaluate bone preservation using implants with different geometry placed into extraction sockets in the maxilla.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21(1):13-21.
[24] Caneva M, Salata LA, de Souza SS,et al.Influence of implant positioning in extraction sockets on osseointegration: histomorphometric analyses in dogs.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21(1):43-49.
[25] Araújo MG, Sukekava F, Wennström JL,et al.Tissue modeling following implant placement in fresh extraction sockets.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006;17(6):615-624.
[26] 周磊.上颌前牙区即刻种植的临床体会[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 2013,48(4):207-210.
[27] 刘宝林.研究生规划教材:口腔种植学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2011:199-200.
[28] 周磊.即刻种植术中引导骨增量技术的应用[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2012,5(4):197-202.
[29] Bersani E, Coppede AR, de Paula Pinto Prata HH.Immediate loading of implants placed in fresh extraction sockets in the molar area with flapless and graftless procedures: a case series.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2010;30(3):291-299.
[30] 林野.即刻种植的是与非[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 2013,48(4): 193-199. |